题记:每次更新hexo博客都要执行三个命令:
- hexo clean
- hexo g
- hexo d
这显然是重复到不行的重复操作,作为一个有极客精神的伪极客爱好者,自然是无法忍受的,所以今天就来研究使用node开发shell(命令行)程序。
search
学习,自然要先查资料,打开google,看到我们熟悉的阮一峰老师的名字,于是决定今天第一个就是它了:Node.js命令行程序开发教程
start
可执行脚本
同样先新建一个hello文件,使用js语言写入:
1 | #!/usr/bin/env node // 保证linux中同样可以使用 |
然后修改 hello 的权限:
1 | $ chmod 755 hello |
就可以执行了:
1 | $ ./hello |
如果想把 hello 前面的路径去除,可以将 hello 的路径加入环境变量 PATH。但是,另一种更好的做法,是在当前目录下新建 package.json ,写入下面的内容。
1 | { |
然后执行 npm link 命令,这时候可能会有杀毒软件提示攻击,不要在意,允许操作就好:
1 | $ npm link |
现在再执行 hello ,就不用输入路径了。
1 | $ hello |
命令行参数的原始写法
命令行参数可以使用node.js提供的系统变量 process.argv 获取;
1 | #!/usr/bin/env node |
执行时,直接在脚本文件后面,加上参数即可:
1 | $ ./hello tom |
上面的代码中实际执行的是 node ./hello tom, 对应的 process.argv 是 [‘node’, ‘/path/to/hello’, ‘tom’]
新建进程
脚本可以通过 child_process 模块新建子进程,从而执行 Unix 系统命令。
1 | #!/usr/bin/env node |
到这里其实我们已经掌握了关键,就是 child_process 的 exec 函数来执行系统命令,从第二个函数也能看出来是一个异步函数,可以写出如下代码:
1 | #! /usr/bin/env node |
三层回掉很难看,async改造他1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17let runShell = function (str) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
exec(str, (err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(new Date().toLocaleString(), str + 'run success');
resolve();
});
});
}
let runAll = function () {
await runShell('hexo clean');
await runShell('hexo g');
await runShell('hexo d');
}
runAll();
在 Git Bash 中执行:
1 | $ chmod 755 hello |
接着在 package.json 最后加入bin:
1 | ... |
执行 npm link,杀毒软件提示,我们不理他,然后,直接:
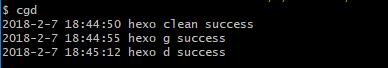
经测试,macos 10.13.6 虽然报了一些错,但依旧可以完美执行我们想要的命令。
2019-01-22 更好的方法
cgd 方案其实已经很方便了,但经过测试,各个平台兼容性不好,具体就是经常报错,再加上每次换电脑都要重新配置很烦人,所以最近经过思考发现也许根本不用那么麻烦。
我们的 shell 命令行本质而言就是一段 node.js 脚本而已,必然而然要在 node.js 环境中运行,而每个 node.js 项目都有自己的 package.json 配置文件,所以这里完全可以使用 配置文件的 script 属性解决:
1 | { |
完全不需要任何配置,命名也分离解耦了,以后每次上传直接一个 npm run up 就解决问题了 :)